For centuries, woodworking has combined artistry with precision. Hand tools shaped intricate carvings, while skilled joinery gave us furniture that stood the test of time. Today, technology is expanding those traditions with new possibilities—and 3D modeling is at the heart of this evolution.
What is 3D Modeling in Woodworking?
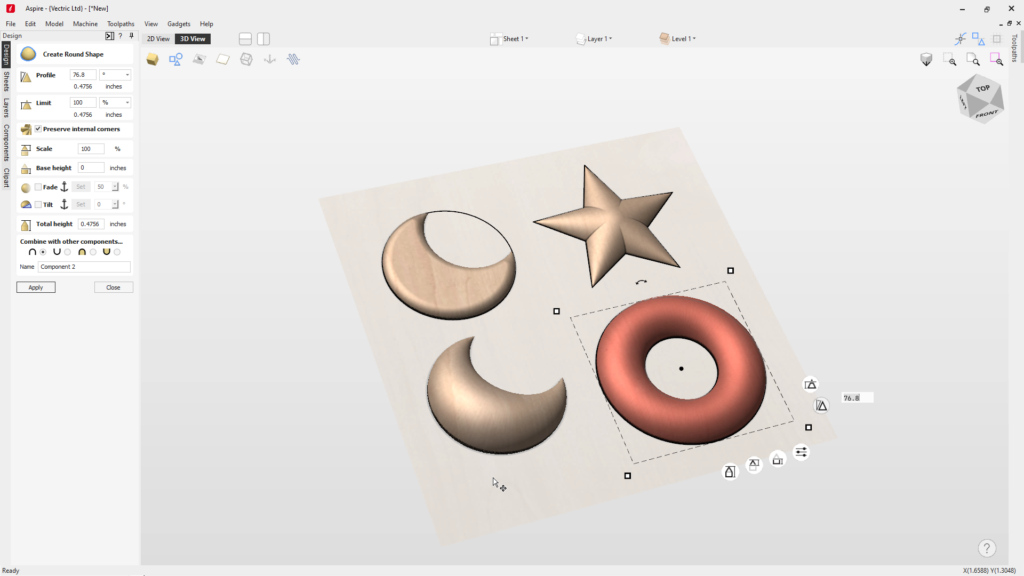
In its simplest form, 3D modeling is the process of creating digital, three-dimensional representations of objects. In woodworking, this means you can design a carving, furniture component, or decorative panel on your computer and preview exactly how it will look before a single board is cut.
Instead of relying solely on sketches and imagination, makers now have the ability to:
- Rotate and view designs from every angle
- Apply realistic textures and patterns
- Simulate how a CNC machine will carve the piece
This not only saves time and reduces material waste but also gives woodworkers more creative freedom.
Why Woodworkers are Turning to Digital Tools
Traditional woodworking skills remain essential, but digital tools like Vectric Aspire add new dimensions to the craft. Aspire allows makers to design detailed relief carvings, custom joinery, and complex textures with accuracy that would take countless hours by hand.
Some practical benefits include:
- Experimentation without risk: You can adjust proportions, change patterns, or test ideas digitally before committing to the material.
- Consistency: Perfectly repeat a design across multiple projects, which is especially useful for professional shops.
- Expanded creativity: Complex geometries and textures become possible, even for small workshops.
Real-World Applications of 3D Modeling
Woodworkers use 3D modeling in a variety of ways:
- Furniture Making: Create detailed legs, moldings, or custom joinery.
- Decorative Carving: Design reliefs, signage, or intricate patterns.
- Prototyping: Visualize how a piece fits in a space before construction.
- Production Efficiency: Prepare toolpaths for CNC machines to streamline workflow.
For many, it bridges the gap between imagination and execution.
How to Get Started
Learning 3D modeling doesn’t require advanced tech skills. Programs like Vectric Aspire are built for makers and prioritize usability. A good first step is experimenting with basic shapes, toolpaths, and simple carvings.
The key is practice: start with small projects, test your results, and gradually build complexity. Pairing this with woodworking fundamentals ensures you maintain the craftsmanship that makes the work truly yours.
Continuing the Tradition Through Innovation
Woodworking has always adapted to the tools of its time. Just as the table saw and router once revolutionized the workshop, today’s digital modeling tools expand what’s possible. For hobbyists, it means pushing creativity further. For professionals, it can transform efficiency and production.
At the North Carolina Furniture School, we’ve seen how empowering 3D modeling can be for students and makers alike. Our upcoming course, Introduction to 3D Modeling with Vectric Aspire, is designed for woodworkers ready to explore this technology in a hands-on, supportive environment.
If you’re curious about what 3D modeling can bring to your craft, this might be the perfect place to begin.
